What the Cognitive Era of Computing Means for Businesses

The cognitive era merges artificial intelligence and computers' immense strengths with the wonders of the human brain and human intelligence. It’s a collaboration between man and machine to solve the next generation of challenges, from how we communicate, to determining the role of cognitive technologies in business processes and decision-making, both predictive and reactive.
In the second part of our cognitive era blog series, we dive into the role of cognitive computing, machine learning, and natural language processing in business and the customer experience. We dive into how cognitive science can inform businesses on improving customer engagement and sentiment. (You can find the first part here.)
Consumers in the cognitive era
Cognitive Computing & Business Benefits
Advertising and customer acquisition have made giant strides in understanding the market and individual consumers. Thanks to today’s algorithms (and applications of cognitive computing), businesses can track activity, target demographics, and identity, and automate marketing messages based on basic parameters.
Businesses today have a wealth of unstructured data at their fingertips, which makes it incredibly challenging to make sense of. Cognitive services open the doors to understanding their customers more deeply and making data-driven decisions based on that data. They can predict and forecast with much greater accuracy and track trends from any data sources across the organization. They can help the human brain make sense of complex problems.
But it’s not just the capabilities of the cognitive systems. It’s also their relation to real-time data streaming, which delivers the data as events occur, whether it be an order being placed, a change in temperature, or a new customer coming on board. Businesses can now gain immediate insight into customer action and performance and make fast, in-the-moment decisions to capitalize and beat the competition.
Talk to an Expert
Let's connect to discuss your real-time project.
Cognitive Science and its Benefits for Consumers
The cognitive era didn’t just usher in a new way to understand customers and the business itself. It also created value for the end users by delivering enhanced experiences.
Take Amazon as an example. Their site has helpful, intelligent automated bots that will make recommendations and ans
wer questions anytime. Wearables like your Apple Watch will deliver curated offers based on proximity. Voice-controlled personal assistant products like Siri can be the gateway to ordering products, controlling your home, making plans, and finding important information.
Conversational interfaces are already becoming a mission-critical gateway for end users to engage with businesses and organizations, regardless of whether a user is interfacing with a store to facilitate a product return and refund or a healthcare provider discussing and providing additional reading material after a recent diagnosis.
Think of an end user interacting with a business that sells car parts. It’s incredibly powerful that a chatbot can continue to build a relationship with an end-user based on prior conversations and factoring in historical activity and demographic information, mimicking the human thought process. At the chatbot’s beck and call is the entire business’s database of products, stock data, other customer data, and more—all that can be used to tailor targeted responses to the end user. This creates an experience more tailored and faster than any human service agent could provide (not to mention no worries about headcount. The bot is always available!)
For consumers, cognitive services power the everyday experiences of using apps. Thanks to the learning algorithms, they continuously grow smarter, deliver more value, and improve relationships between businesses and end users.
Implementation
Big data input and processing
For businesses that create massive amounts of data, for example, IoT, home automation companies, or financial firms, we have great technology for ingesting and processing the data generated by huge deployments of connected devices. Cognitive services sit in the middle before the data is stored and analyze the data for your use case, but can also create events if you’re using an event driven architecture.

Diagram explanation: In a big data use case, the cognitive service, in this case, IBM Watson, processes the data coming through the firehose. The service can reroute the processed data. At the same time, it’s in motion, delivering certain analyses to a visualization, an event to any number of other containers, and other data to store.
Real-time data streams
Cognitive services greatly impact apps, allowing users to communicate in real time or any deployment where small amounts of data are streamed in sub-second deliveries. This enables businesses to execute business logic, in this case, trigger their cognitive services, directly in the data stream, manipulating, filtering, and analyzing that data and delivering a transformed version to an end user.
Take chat. We know that chat has been transformed and that cognitive services play a massive role in that evolution. Integrating cognitive services into messaging feeds lets you do amazing things with the data. You can translate any language into any language, turn text into natural speech (or vice versa), or even analyze the sentiment of messages coming through a chat feed.
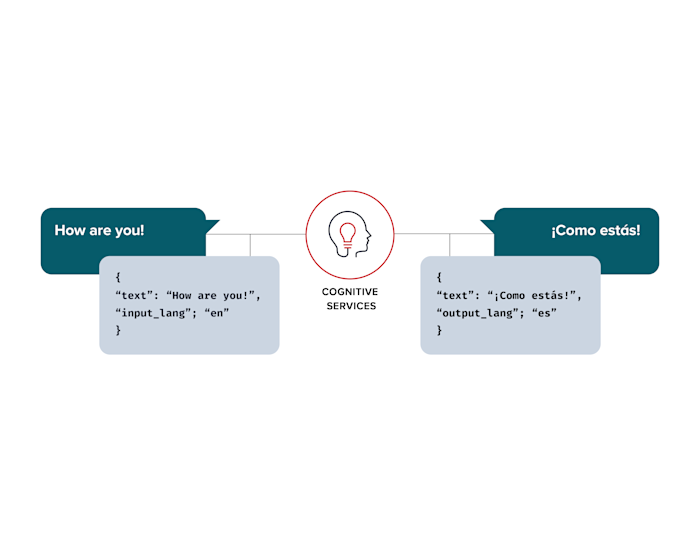
Diagram explanation: In this use case, the cognitive service sits between the chat users. Instead of sending the raw message to an external server, having it translate the message, and sending the processed message to the recipient, the translation and other optimizations take place directly in the middle, decreasing latency and reducing unnecessary infrastructure.
Cognitive Computing at the edge
Edge computing is computing as close to the data source as possible, providing an incredibly fast and efficient way to take action on data. Instead of streaming all data to a central data center (i.e., ‘the cloud’), edge computing alleviates the network of potential bandwidth bottlenecks. It processes the data that matters, keeping it close to the source.
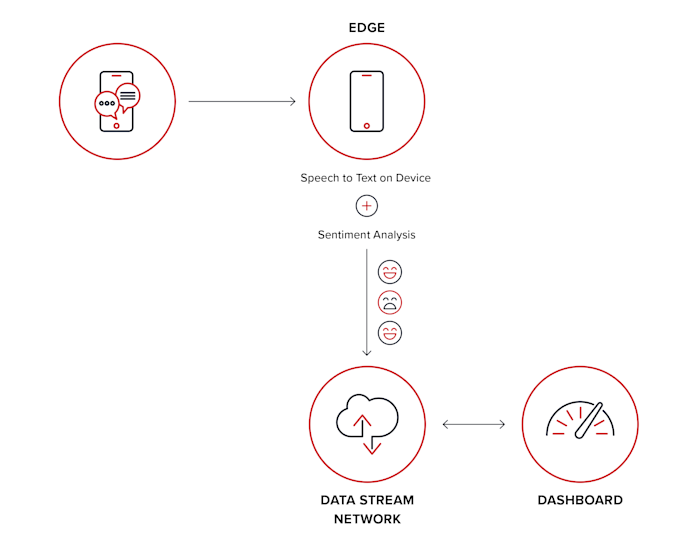
Diagram explanation: In this use case, the cognitive service sits on the device, where all processing occurs. The end device takes the speech, converts it to text, and analyzes the message's sentiment using natural language processing. This way, the device on the edge only has to send the sentiment data to the dashboard and doesn’t have to send the actual contents of the message, which shortens the workflow.
A world transformed
Cognitive services have transformed apps and businesses alike. They work more efficiently, safely, and sustainably, delivering more engaging and immersive customer experiences. From the way we buy goods, to the way our children learn, to the food we eat, cognitive services drive the innovation of industries and organizations into the future and give those who quickly adopt (and adapt), a competitive advantage.


